1. CMM, EOO, GQQ, _____, KUU
A. GRR
B. GSS
C. ISS
D. ITT
2. QPO, NML, KJI, _____, EDC
A. HGF
B. CAB
C. JKL
D. GHI
Direction (3 - 5): Choose the pair that best represents a similar relationship to the one expressed in the original pair of words.
3. BINDING : BOOK
A. criminal : gang
B. frame : picture
C. display : museum
D. artist : carpenter
4. PETAL : FLOWER
A. salt : pepper
B. tire : bicycle
C. base : ball
D. sandals : shoes
5. WAITER : RESTAURANT
A. doctor : diagnosis
B. actor : role
C. teacher : school
D. driver : truck
Direction (6 - 7): Choose the picture that would go in the empty box so that the two bottom pictures are related in the same way as the top two are related.
6.
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
7.
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Direction (8 - 9): Which one set of letters when sequentially placed at the gaps will complete the given letter series?
8. a b _ c a b b _ a b b _ a b _ c
A. aabc
B. aaab
C. accb
D. bccb
9. a b c _ b c _ a b c c _ a _ c c c c
A. accb
B. abbc
C. bcca
D. accc
10. In a certain code language, UNDER is coded as VPGIW. How is SOME coded in the same language?
A. TPQH
B. TQPI
C. TOPJ
D. TPQH
11. In a certain code language, SMART is coded as RNZSS. How is NAÏVE coded in the same language?
A. MBHWD
B. OZJUF
C. OBHUF
D. MBHVE
12. In a certain code language, LAME is coded as 31. How is DULL coded in the same language?
A. 84
B. 74
C. 64
D. 49
13. A $ B means A is the father of B;
A # B means A is the sister of B;
A * B means A is the daughter of B;
A @ B means A is the brother of B.
Which of the following indicates that M is the wife of Q?
A. Q $ R @ T * M
B. Q $ R @ T # M
C. Q $ R # T @ M
D. Q $ R * T # M
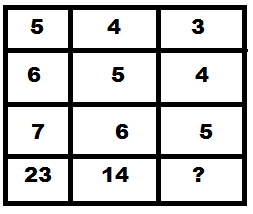
Direction (14 - 15): Find out the missing number from the given options.
14.
A. 40
B. 45
C. 50
D. 55
15.
A. 7
B. 12
C. 17
D. 23
Answers Key:
1. (C): The first letters are in alphabetical order with a letter skipped in between each segment: C, E, G, I, K. The second and third letters are repeated; they are also in order with a skipped letter: M, O, Q, S, U.
2. (A): This series consists of letters in a reverse alphabetical order.
3. (B): A binding surrounds a book; a frame surrounds a picture.
4. (B): A petal is a part of a flower; a tire is a part of a bicycle.
5. (C): A waiter works in a restaurant; a teacher works in a school.
6. (D): An oar is to a canoe as a steering wheel is to a car. This is a functional relationship. The oar helps steer the canoe in the way that the steering wheel steers the car.
7. (B): A toddler is to an adult as a caterpillar is to a butterfly. This relationship shows the young and the adult. The caterpillar is an early stage of the adult butterfly.
8. (D): The sequence given is a b b c a b b c a b b c a b b c
9. (A): The sequence given is a b c a b c c a b c c c a b c c c c
10. (B): According to the alphabetical sequence, each letter in the word UNDER is shifted to its right by 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 places respectively.
11. (A): In the word SMART, each odd places letter is shifted 1 place to its left while each even placed letter is shifted to its right according to their alphabetical sequence. So, by following the same pattern for the word NAIVE, the corresponding code will be MBHWD
12. (D): Taking A=1, B=2, C=3 and so on, we can see that 31 is the sum of the positions of LAME.
13. (A):
14. (C):
(1 + 7) * (1 + 5) = 48;
(1 + 9) * (1 + 6) = 70;
(2 + 3) * (1 + 9) = 50
15. (A):
5 * 6 - 7 = 23;
4 * 5 - 6 = 14;
3 * 4 - 5 = 7




No comments:
Post a Comment