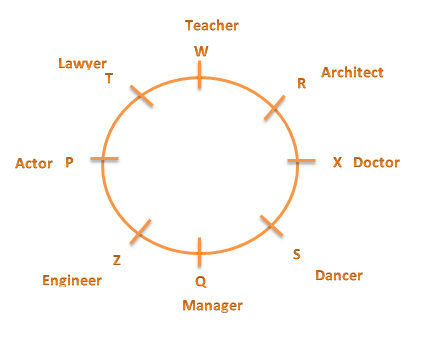
Directions (1-7): Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions:
Eight friends P, Q, R, S, T, W, X and Z are sitting around a circular table facing the centre but not necessarily in the same order. Each one of them belongs to a different profession viz. Engineer, Architect, Dancer, Teacher, Lawyer, Manager, Actor and Doctor.
T sits third to right of the Doctor. Only two people sit between the Doctor and Z. Teacher and the Architect are immediate neighbours of each other. Neither T nor Z is a Teacher or a Architect. Teacher is not an immediate neighbour of the Doctor. Engineer sits second to left of S. S is not an immediate neighbour of Z. The Engineer is an immediate neighbour of both Manager and the Actor. Actor sits third to right of R. R is not the Teacher. X sits to the immediate right of the Dancer. T is not the Dancer. Q is not an immediate neighbour of T. W is not an immediate neighbour of the Engineer
1. Which of the following is true with respect to the given seating arrangement?
1) The Manager is an immediate neighbour of the Teacher.
2) W sits second to right of P.
3) The Manager and the Architect are immediate neighbours of each other.
4) The Dancer sits to the immediate left of the Doctor.
5) The Manager sits second to the left of P.
2. Which of the following is R’s profession?
1) Dancer
2) Engineer
3) Architect
4) Lawyer
5) Actor
3. Who amongst the following sit exactly between the Doctor and Z?
1) Z and the Dancer
2) R and W
3) The Dancer and X
4) Q and X
5) S and the Manager
4. Who amongst the following is the Manager?
1) X
2) Q
3) W
4) Z
5) T
5. Who amongst the following sits third to the left of S?
1) Engineer
2) W
3) T
4) Actor
5) R
6. Four of the following five are alike in a certain way based on the given arrangement and thus form a group. Which is the one that does not belong to that group?
(1) Q - Dancer
(2) W - Teacher
(3) P – Engineer
(4) T - Actor
(5) R - Doctor
7. Who amongst the following is the Teacher?
1) T
2) X
3) Z
4) W
5) P
Directions (8-10): Read the following information given below to answer the questions that follow:
(i) 'na ho pa la' means 'they are very intelligent'
(ii) 'pit na sa' means 'you are welcome'
(iii) 'ka da la' means 'who is intelligent'
(iv) 'od ho pit la' means 'they welcome intelligent students'
8. Which of the following means 'students' in that code language?
(1) od
(2) la
(3) ho
(4) pit
(5) Data inadequate
9. Which of the following means 'very' in that code language?
(1) pa
(2) na
(3) da
(4) Data inadequate
(5) None of these
10. Which of the following statement(s) is/are redundant to answer the above questions?
(1) (iii)
(2) (ii)
(3) (ii) or (iii)
(4) (i) or (iv)
(5) None of these
Answers
Solution (1-7)
1.4
2.3
3.5
4.4
5.2
6.4
7.2
Solution (8- 10)
students – od
intelligent – la
welcome – pit
they – ho
are – na
you – sa
very – pa
who / is – ka / da
8.1
9. 1
10.1